Experimental probability is probability that is determined on the basis of the results of an experiment repeated many times.
Theoretical probability is probability that is determined on the basis of reasoning.

Experimental probability is probability that is determined on the basis of the results of an experiment repeated many times.
Theoretical probability is probability that is determined on the basis of reasoning.

Probability is a value between (and including) zero and one.
If P(E) represents the probability of an event E, then:
If n(S) represents the number of times an experiment is executed, and n(E) represents the number of times event "E" occurs, then in this context P(E) represents the experimental probability that event E will occur and is given by:
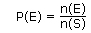
The more times the die is tossed, the closer the values of the experimental probabilities get to the values of the theoretical probabilities (of getting a chosen numeral).
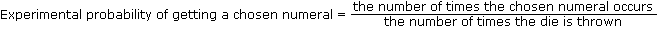
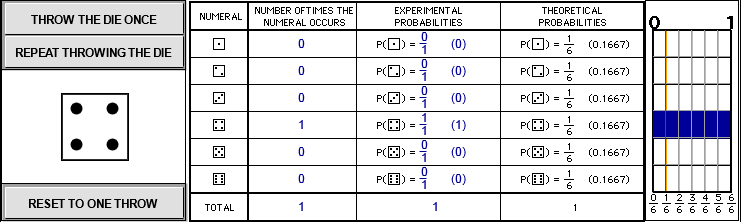 Image onlyInstructions text as in global.js
Image onlyInstructions text as in global.jsThe more times the spinner is spun, the closer the values of the experimental probabilities get to the values of the theoretical probabilities (of landing in each sector).
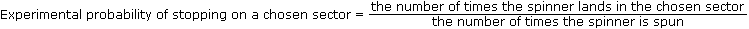
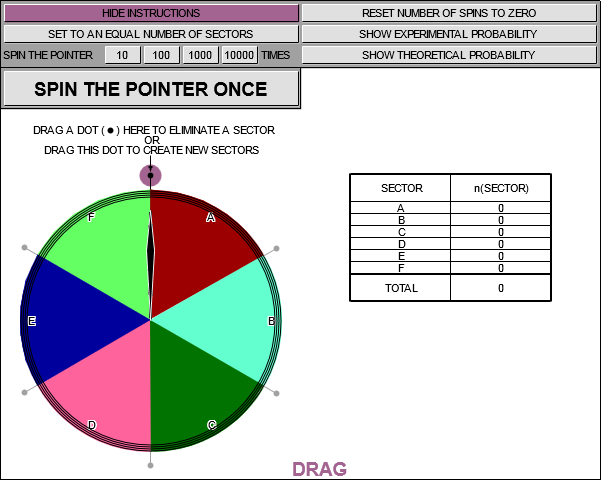 Image onlyInstructions text as in global.js
Image onlyInstructions text as in global.js