A circle is the locus of points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point in the plane. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle. The constant distance is called the radius of the circle.
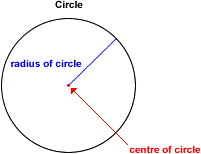
A circle is the locus of points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point in the plane. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle. The constant distance is called the radius of the circle.

The standard form of a circle with centre(h, k) and radius r is (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2.
The standard form is derived from the definition of a circle in conjunction with the distance formula.
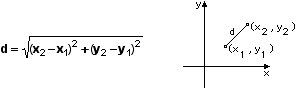
If the centre is labeled as (h, k) and the constant distance is defined to be r, then the following results.
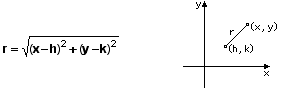
By squaring both sides of the equation, (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2 results.
The general form of a quadratic relation is Ax2 + Bxy + Cy2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0. A quadratic relation will result in a circle, or degenerate circle, when A = C and B = 0.
A circle will result from the intersection of a right circular cone (or cylinder) and a plane perpendicular to the axis of the cone (or cylinder).
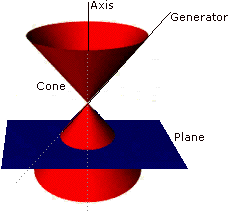
Select the animations below to better visualize the relationship of the circle to conic sections.