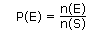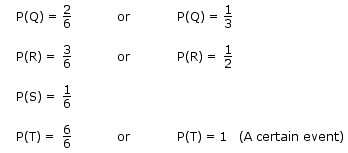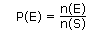
An event is one or more outcomes of a probability experiment.
In an experiment of tossing a die, there are six possible outcomes.
A listing of all of the outcomes of an experiment is called the sample space (S) of the experiment.
If each face is represented by a numeral of the number of dots on the face; the following represents the sample space for this experiment:
S: { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }
Any of the six outcomes is an event. Note that groups of outcomes can also be an event. Some examples are given below:
Event Q: Getting a 1 or a 2.
Event R: Getting an even number (2 or 4 or 6).
Event S: Getting a 3.
Event T: Getting a 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6.
If n(S) represents the number of outcomes in the sample space [n(S) = 6] and n(E) represents the number of outcomes in event E, then: