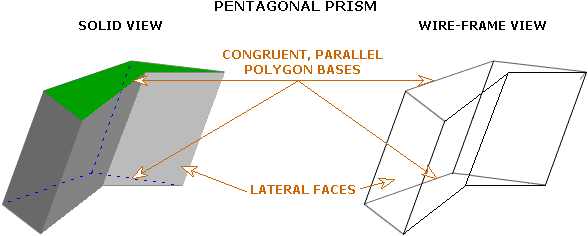
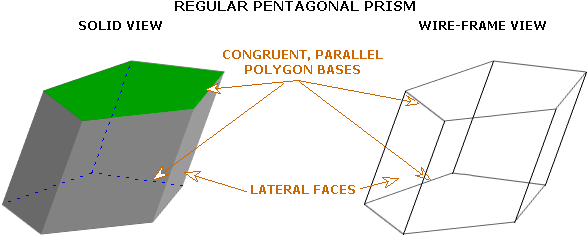
A prism is a three-dimensional object with two congruent, parallel polygon bases. The remaining faces are parallelograms coresponding to each side of a base. The faces which are not bases are called lateral faces.
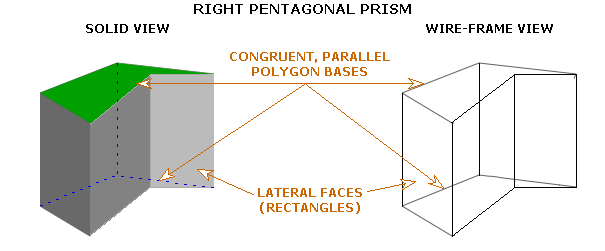
A right prism is a prism with one of the bases aligned directly above the other so that all of the lateral faces are rectangles.
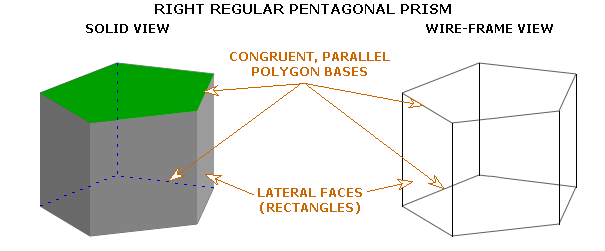
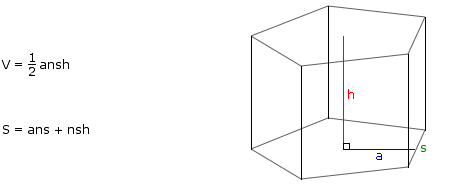
Usually right prisms with triangular bases, rectangular bases or bases which are regular polygons are studied. In the example below, the base is a regular pentagon. Note that each lateral face of a right prism is a rectangle.
In general, the volume of a prism is the area of the base times the height of the prism.
In general, the surface area of a prism is the sum of the areas of all of the faces of the prism.
Prism with a Regular Polygon Base
a: The length of an apothem of the base of the prism
n: The number of sides of the base of the prism
s: The length of a side of the base of the prism
h: The height of the prism
V: The volume of the interior of the prism
S: The surface area of the prism
Explanation of volume formula (regular polygon base)
Explanation of surface area formula (regular polygon base)