 Grade 8
Grade 8
Perfect Squares and Square RootsStep 4: Assess Student LearningGuiding Questions
Sample Assessment TasksIn addition to ongoing assessment throughout the lessons, consider the following sample activities to evaluate students' learning at key milestones. Suggestions are given for assessing all students as a class or in groups, individual students in need of further evaluation and individual or groups of students in a variety of contexts. A. Whole Class/Group Assessment Examples of Whole Class/Group Assessment B. One-on-One AssessmentActivity 1: Solve the following problems. Solutions should contain diagrams and written explanations.
C. Applied LearningProvide opportunities for students to use the knowledge they have gained about perfect squares and square roots and notice whether or not this knowledge transfers. Activity 1: Given the area of a square, find the side of the square and the perimeter. Activity 2: Apply knowledge of square roots with right triangles and the Pythagorean theorem. Related Resources |
|||||||









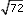 lies between which two whole numbers? Explain how you know. Sketch a number line to show your answer.
lies between which two whole numbers? Explain how you know. Sketch a number line to show your answer.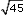 ?
?
